Why monitoring freight rate forecasts is crucial for your logistics planning in Q4 2025
As we enter the final quarter of 2025, freight rate forecasts have become more critical than ever for shippers navigating an increasingly complex global logistics landscape. The Q4 2025 freight market presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities, shaped by tariff uncertainties, capacity dynamics, and evolving demand patterns across all transportation modes.
Recent data shows a sharp divergence across freight sectors: ocean rates on Asia–Europe routes have plunged, while air freight remains relatively elevated, and North American truckload spot rates are expected to edge up modestly in Q4.
Understanding these freight market trends is essential for logistics managers planning their Q4 operations. This comprehensive guide provides data-driven insights into shipping rates forecasts, strategic recommendations, and expert predictions to help you optimize costs and maintain supply chain resilience through year-end and into 2026.
Understanding Freight Rate Dynamics in Q4 2025
Late Q4 2025 freight rate forecast are shaped by a complex interplay of economic conditions, operational challenges, and external forces. Navigating these dynamics requires flexibility and insight into the key factors influencing market shifts, which are outlined in the following sections. This understanding will help shippers anticipate changes and adjust strategies accordingly to maintain competitiveness and cost efficiency.
Key factors influencing freight rates this quarter
The Q4 2025 freight rate forecast is driven by interconnected factors creating market complexity, with trade policy uncertainty and tariffs dominating, influencing cargo flows and frontloading on major lanes.
Capacity varies by mode: Ocean faces overcapacity (8% fleet growth vs. 3% demand), pressuring rates downward despite Red Sea diversions; air freight sees 2-4% capacity growth against 6-10% demand, pushing rates up; North American trucking tightens as carriers exit, with the Driver Availability Index improving for the first time in three years.
Seasonal demand patterns are unpredictable, with muted peak surcharges, but tariff uncertainty spurs sporadic front-loading and capacity squeezes, especially in air cargo on Asia-Europe routes amid 58% year to date e-commerce surge.
Global economic indicators and their impact on shipping costs
Global macroeconomic conditions are providing mixed signals for freight cost predictions. October Q4 GDP growth projections increased 0.6% from July forecasts, representing a nearly 30% upward revision. Real export projections have been revised up to 2.98% globally, with significant increases from China and the APAC region.
However, freight-intensive sectors are underperforming broader economic growth. Manufacturing indexes in China, the United States, and Europe all came in below expectations in Q2, with industrial production remaining mostly flat at 2.10%. Retail sales forecasts increased to 1.74%, showing growth from the US and Europe, but consumer confidence remains subdued, particularly in the American market where inflation concerns persist.
Ocean Freight Rate Forecast Q4 2025
Entering Q4 2025, the ocean freight sector remains challenged by persistent overcapacity and evolving trade flows. Carriers and shippers alike are navigating a cautious environment where rate stability takes precedence over recovery, amid fluctuating demand and ongoing geopolitical influences.
Container shipping rates: Current trends and predictions
The ocean freight rates forecast for Q4 2025 points to continued rate pressure despite persistent Red Sea disruptions. The Drewry World Container Index has dipped to approximately $1,859 per 40-foot container, down 5% weekly but still nearly double pre-pandemic levels. Structural overcapacity (8% capacity growth versus 3% demand) overrides Red Sea effects, per Xeneta, leading to spot rate declines of 15-20% quarter-over-quarter. Contract rates are aligning with spots for greater transparency, with baseline forecasts pointing downward unless additional strikes emerge; Veson anticipates a decline as new vessels flood the market.
Regional breakdown: Asia-Europe, Trans-Pacific, and other major routes
Below is a clear snapshot of how major global trade lanes are evolving, highlighting recent rate movements and operational dynamics across the Asia-Europe corridor, Trans-Pacific routes, and other key regions.
- Asia-Europe lane: Rates have edged up 3% to $2,038 per 40ft (Shanghai-Rotterdam), with carriers like MSC eyeing $3,100 from December amid volume expectations, though down 60% year-over-year overall.
- Trans-Pacific routes: Spot rates fell 15% to $3,254 per 40ft (Shanghai-New York), reflecting softened demand; traditional differentials between coasts are eroding due to reallocations.
- Other Routes: Intra-Asia remains stable with modest growth from nearshoring; Latin America grapples with congestion at Buenaventura and low Amazon River levels.
Trade Lane | Current Rate (per 40ft) | YoY Change |
Asia-Europe | $2,038 | -60% |
Trans-Pacific | $3,254 | -70% |
Intra-Asia | Stable | Modest growth |
Peak season impact on ocean freight costs
The 2025 peak season has been one of the weakest in years for ocean freight rates. Usual Q3/Q4 rate hikes tied to holiday demand have been minimal because capacity continues to exceed shipping needs, and retailers have avoided major restocking. Peak Season Surcharges (PSS) have stayed low at $300–$2,000 per container, reflecting ongoing structural overcapacity. Carriers are increasingly using blank sailings, especially around China’s Golden Week, to manage this imbalance.
Although the National Retail Federation raised Q4 volume forecasts due to some front-loading ahead of possible strikes and tariffs, the added demand hasn’t meaningfully lifted rates. Looking to 2026, if Red Sea disruptions end and Suez traffic normalizes, even greater overcapacity could push some ex-Asia rates below $1,000 per FEU.
DocShipper Alert
Freight rates are experiencing sudden fluctuations due to maritime overcapacity, rerouting via the Cape of Good Hope, and US-China tariff uncertainties.
Don’t let this instability impact your profitability.
👉 With DocShipper, secure your capacity, anticipate price increases, and optimize your costs thanks to our forecasting tools and negotiated contracts.
Contact us now for a free analysis of your logistics costs.
Air Freight Rate Forecast Q4 2025
As the air freight market approaches the final quarter of 2025, shippers face a delicate balance between steady demand and capacity constraints,with e-commerce and seasonal boosts providing steady support. Rate fluctuations are expected due to evolving trade patterns, regulatory changes, and operational challenges, making careful planning essential for managing costs and securing reliable service.
Air cargo market overview and pricing trends
Q4 2025 air freight rates forecast remain stable but elevated. Global air cargo rates fell 5.8% year-over-year in September and have stayed mostly flat after strong demand growth in 2024. Despite this, spot rates ended 2024 up 15%, and 2025 is marked by “cautious optimism” with ongoing geopolitical risks. Capacity is expected to grow only 4–5% while demand may rise 6–10%, keeping the market tight and prices supported.
Rate movements vary by region: China–North America fell 5% to $5.30/kg, China–North Europe rose 5% to $3.70/kg, and Europe–North America saw sharp swings, spiking 21% in December before dropping 25% in early January due to airlines shifting freighter capacity toward Asia–Europe e-commerce flows.
E-commerce and seasonal demand effects on air freight rates
E-commerce remains the main engine of air freight demand, but trade flows are shifting. Chinese platforms have redirected volume from the U.S. to Europe, where e-commerce imports have doubled. Low-value shipments from China to Europe jumped 62% year-over-year in September, far above the overall e-commerce growth rate of 18%.
Meanwhile, China–U.S. e-commerce air shipments fell for the fifth straight month, down 34% year-over-year, driven by potential U.S. de minimis policy changes that threaten the $800 duty-free threshold. Forecasts diverge: Accenture expects 10% Q4 demand growth, while others project a more modest 3–4% for 2025.
The typically strong September product-launch season was weaker due to softer U.S. consumer sentiment. High-tech shippers are advised to secure capacity 3–4 weeks before production finishes to avoid delays during the tight Q4 cycle.
DocShipper info
E-commerce from China to Europe is booming (+62% year-over-year), saturating cargo flights.
As a result, there are high rates and limited capacity in Q4.
👉 DocShipper optimizes your shipments:
- Pre-booking 3–4 weeks before production,
- hybrid options (express + deferred air),
- Real-time tracking
- securing capacity with multiple carriers.
Road and Rail Freight Market Outlook
The road and rail freight markets continue to evolve in response to economic shifts, infrastructure investments, and regulatory changes. Understanding the outlook for both modes is essential for shippers seeking to optimize their logistics strategies in a dynamic transportation environment.
Trucking capacity and rate predictions
The North American truckload market is slowly rebounding after a prolonged freight recession. ACT Research’s Driver Availability Index tightened for the first time in three years, signalling emerging supply constraints that are helping stabilize freight rates. September spot rates held steady at $1.63/mi for dry van, $1.92 for reefer, and $2.18 for flatbed, reflecting end-of-quarter shipping rather than true demand growth. C.H. Robinson expects spot rates to rise 5–10% year-over-year in Q4 due to seasonal trends and continued carrier exits.
Contract rates are also under upward pressure as operating costs keep climbing. ATRI reports truckload costs rose nearly 4% in 2024 (excluding fuel), on top of a 25% inflation buildup over the past three years. These structural cost increases will continue to push rates higher during periods of disruption, even as overall supply and demand remain relatively balanced.
Intermodal freight trends for Q4 2025
Intermodal volumes are forecast to grow 3% in 2025, with pricing increasing in Q4 due to tariffs and strong rail service performance. The intermodal sector benefits from improved schedule reliability, with major carriers focusing on hub-and-spoke networks centered on major ports.
TD Cowen/AFS Freight Index forecasts LTL carriers will continue cost-effective rate pricing and network efficiency through year-end. LTL demand remained down 4% year-over-year through H1, but the sector remains healthy with good alternatives for shippers. General rate increases (GRIs) are expected to remain in the 3-5% range, though they may be negotiable.
Factors Driving Freight Rate Changes in Q4 2025
Freight rates fluctuations in the final quarter of 2025 are influenced by a complex mix of economic, geopolitical, and operational factors. Understanding these drivers is crucial for shippers aiming to navigate volatility and optimize their logistics strategies as the year closes.
Fuel prices and carrier capacity adjustments
Fuel prices are easing carrier costs in late 2025, with the EIA forecasting crude at $69 per barrel for 2025 (averaging $62 in Q4) and diesel at $3.61 per gallon for the year. While lower fuel costs can reduce operating expenses by 5–10%, weak demand means these savings are mostly boosting carrier margins rather than reducing shipper rates. Fuel represents 20–30% of total costs, making even small declines meaningful.
Capacity trends differ by mode: ocean carriers continue ordering new vessels despite oversupply, signaling further rate pressure into 2026; air cargo capacity remains limited due to delayed freighter deliveries and airlines favoring passenger routes; and trucking capacity is shrinking through carrier exits, with Class 8 tractor orders down 44% year-over-year in September, especially in California.
Geopolitical tensions and trade policy impacts
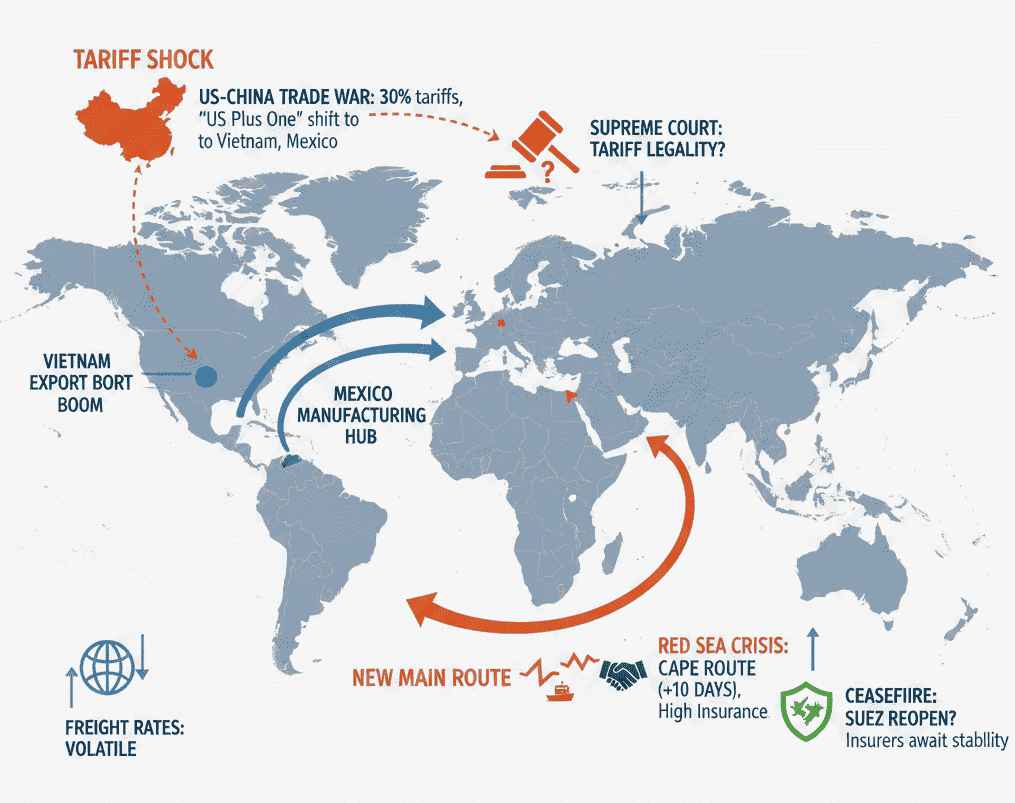
Tariff policy remains the biggest source of uncertainty for freight rate forecasts. After the April 2025 Liberation Day tariff actions, the market has largely paused, awaiting clarity. A U.S. appeals court ruled that using IEEPA for tariffs is illegal, but existing tariffs stay in place pending a Supreme Court decision.
China’s decision to send a top negotiator to Washington after a 90-day extension of 30% baseline U.S. tariffs suggests movement, though any volume shift will be slow. The uncertainty is weighing heavily on China–U.S. trade, pushing companies toward “US Plus One” models that pair domestic operations with offshore production.
Meanwhile, the Red Sea crisis has shifted from short-term shock to a long-term operating condition. Despite ongoing attacks and Cape of Good Hope rerouting, carriers have adapted. A preliminary May 2025 ceasefire raises the possibility of Suez Canal reopening, but insurers will need sustained stability before restoring coverage.
Holiday season demand and inventory strategies
Holiday season demand for Q4 2025 is unusually hard to predict, as consumer spending remains soft and businesses avoid heavy pre-season inventory builds. The National Retail Federation raised December volume estimates, but mainly due to front-loading rather than real demand strength.
Companies are leaning into just-in-time inventory strategies, reducing peak season freight but increasing volatility when demand spikes. Retailers are keeping inventories lean and relying more on expedited shipping to react to actual sales.
The typical September NPI season was also weaker, with major brands delaying launches amid uncertain sentiment. As a result, the air cargo peak has softened, though product-launch shippers should still secure core capacity while keeping backup options for expedited moves if demand surprises.
DocShipper Advice
Air and road rates remain high, but smart multimodal options (sea + air, rail + road, or sea + rail) unlock major savings without extending delivery times. Acting before seasonal peaks lets you secure capacity and negotiate better terms.
👉 DocShipper designs your customized multimodal strategy to optimize every shipment through:
- Up to 20% cost reduction thanks to strategic route combinations.
- Reliable transit times comparable to single-mode shipping.
- Increased resilience to market and route disruptions.
Adapt faster, ship smarter. Request your customized strategy!
Industry Expert Forecasts and Market Analysis
Leading freight market analysts converge on a challenging Q4, blending predictions with historical context for clarity.
What major freight analysts predict (Freightos, Veson Nautical, C.H. Robinson)
ACT Research (whose Cass Linehaul Index forecasts have been 98.8% accurate) expects the for-hire rate recession to be ending, though recovery will be capped by private fleet growth. ACT’s Tim Denoyer notes that rates have softened since mid-May and capacity has remained ample even during peak seasonality, but tightening driver availability should help limit further declines.
Freightos anticipates continued downward pressure on ocean rates, with structural overcapacity likely to push ex-Asia prices back below $1,000/FEU once Red Sea disruptions ease.
C.H. Robinson expects modest truckload spot rate increases in Q4, driven by seasonality and rising carrier costs. With operating expenses up 25% over three years, they forecast that rates will remain elevated relative to pre-pandemic norms.
Comparing Q4 2025 rates with historical data
Freight rates are in a transition phase, well below pandemic highs but still above pre-2020 norms. Ocean rates sit at about $2,836 per 40ft container, nearly double pre-pandemic averages but far from the $10,000+ peaks of 2021–2022.
Air cargo spot rates of $3.50–$5.30/kg are also elevated versus 2019 but much lower than pandemic-era highs, with the market stabilizing after strong growth. Truckload spot rates around $1.63/mile have levelled off after hitting 15-year margin lows, while the NTI 7-day average of $2.43/mile shows improvement from 2023 but remains weighed down by excess capacity.
Strategic Recommendations for Shippers
With freight costs predictions climbing amid global uncertainty, shippers must take a proactive approach to optimize expenses and strengthen their supply chains in late 2025
How to optimize your shipping costs in Q4 2025
To optimize shipping costs in 2025, adopt a multi-faceted strategy focusing on procurement, efficiency, and flexibility:
- Ocean Freight: Negotiate aggressive contract rates, as carriers under capacity pressure are eager for committed volumes.
- Air Freight: Build ties with multiple carriers / forwarders for peak access; shift from 90% air models to 60/40 blends of direct fulfillment and forward stock, especially amid e-commerce regulation shifts.
- Technology: Use platforms like Freightos/Flexport for real-time rate comparisons; apply predictive analytics to time bookings and forecast rates.
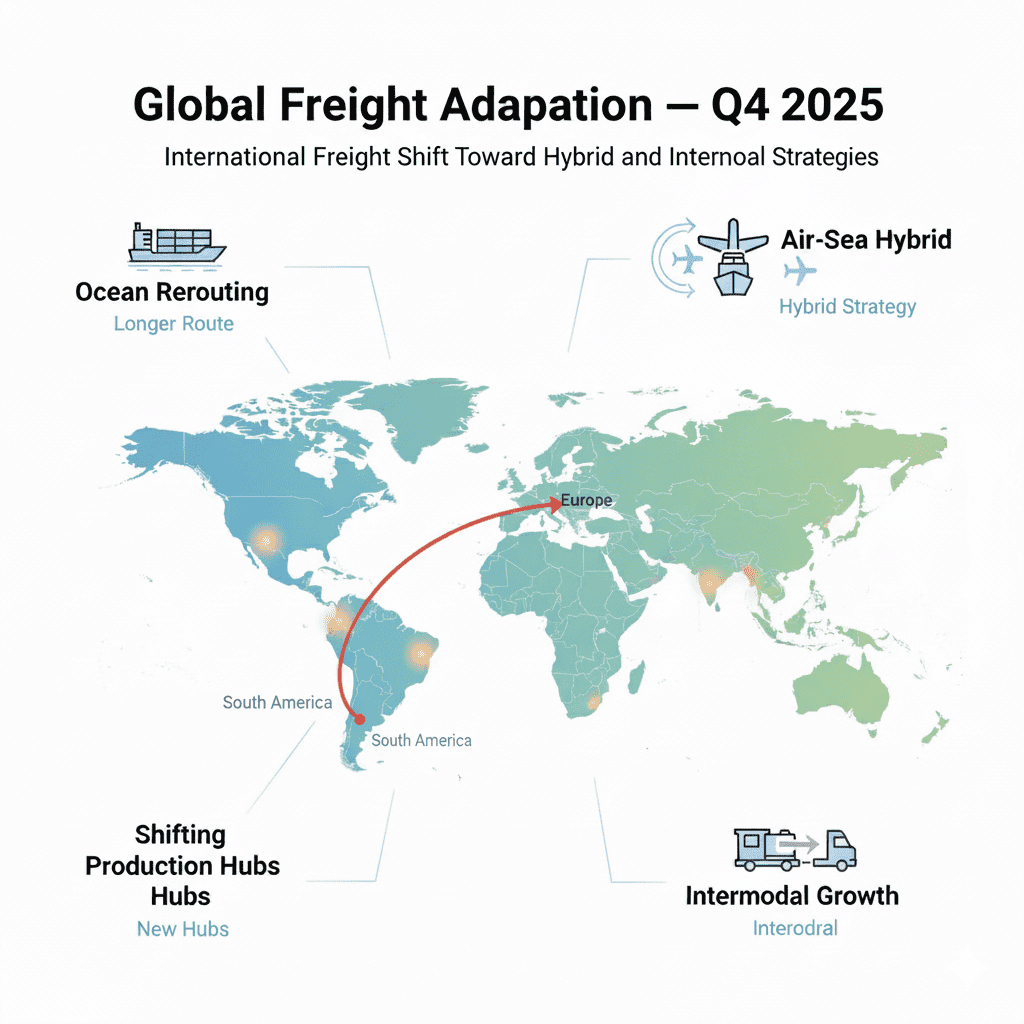
- Diversification: Avoid overreliance on single modes/carriers by maintaining core relationships while shifting volumes as needed for better rates/service.
DocShipper Advice
Tariffs, political shifts, and supply bottlenecks are reshaping global trade. Nearshoring to Vietnam or Mexico helps reduce tariff exposure, balance lead times, and secure sourcing closer to key markets.
DocShipper guides your transition with end-to-end support (supplier sourcing, logistics coordination, and customs expertise) to build a supply chain that’s both resilient and cost-efficient.
Contract negotiation tips and hedging strategies
As supply chains head into 2026, volatility across freight markets demands a contracting strategy that balances cost control with agility. With rate trends diverging across modes and economic signals remaining mixed, shippers need a structure that protects budgets while preserving flexibility:
- Ocean: Prioritize 12-month+ contracts with built-in rate-reduction clauses to mitigate further market softening.
- Trucking: Strengthen relationships with dependable carriers and use targeted mini-bids to stay price-competitive without compromising service.
- Fuel: With oil prices expected to ease, lock in base rates now to benefit from potential downward adjustments.
- Flexibility: Contract 60–70% of your forecasted volume and keep 30–40% for the spot market to capitalize on dips and respond to shifting demand.
Alternative routing and mode selection considerations
Red Sea disruptions continue to redefine global alternative routing patterns. With Cape of Good Hope transits now the reliable standard for Asia–Europe trade, shippers face 1–2 week delays and 15–20% higher costs. Planning should reflect these extended lead times rather than assuming a near-term Suez reopening.
For urgent or high-margin goods, partial air freight offers a practical balance. Ship high-value, low-volume components by air and bulk cargo by sea. Deferred air services can reduce costs by 30–40% compared with express options while still mitigating overall transit delays.
Supply chain diversification remains a top priority. Mexico’s rise as the U.S.’s largest trading partner under USMCA highlights nearshoring’s appeal. Meanwhile, Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia provide competitive alternatives to China within 6–12 months, improving tariff resilience and manufacturing agility.
On the North American front, intermodal transport is regaining traction. For lanes over 750 miles, it can deliver 10–20% cost savings and lower emissions while maintaining reliable service amid 3% forecasted volume growth. Such solutions align economic efficiency with corporate sustainability goals.
Regional Freight Rate Forecasts
Across North America, Europe-Mediterranean, and the Asia-Pacific region, freight markets are evolving under a mix of economic shifts, geopolitical pressures, and changing supply-chain dynamics that are shaping costs and capacity worldwide. Freight dynamics vary by region, demanding localized strategies, outlooks for key areas.
North America freight market outlook
The North American freight market is gradually stabilizing after a downturn, with truckload spot rates expected to rise 5-10% year-over-year in Q4 due to seasonal demand and capacity reductions. Despite this, rates remain below the highs seen in 2021-2022, with dry van spots around $1.63 per mile.
Contract rates face upward pressure from sustained cost inflation, carriers have seen 25% cumulative increases in operating costs excluding fuel over three years, with insurance, wages, and equipment among key drivers. Port congestion has eased to pre-pandemic levels, though infrastructure projects and labor risks remain at some gateways. Nearshoring boosts cross-border freight with Mexico, causing capacity tightness and a 10-15% rate premium in border regions like El Paso and Laredo.
Europe and Mediterranean shipping rates
Improved Rhine River water levels facilitate cost-efficient barging for bulk goods. Brexit continues to add 10-15% in delivery costs due to extra border checks and paperwork, encouraging nearshoring and the growth of European distribution centers.
Asia-Pacific freight cost predictions
The Asia-Pacific freight market remains volatile with China’s slower GDP growth of 4.6% in Q3 2025 weakening export volumes and applying downward rate pressure. However, rapid e-commerce growth (+18%) is shifting demand toward smaller, frequent shipments and driving a 62% increase in air freight demand from China to Europe.
Southeast Asia’s manufacturing strength rises as companies adopt China+1 strategies, with Vietnam’s exports up 14%, leading to premium freight rates on Southeast Asia–U.S. routes due to limited direct connections. Intra-Asia trade grows steadily by 3-4%, but port congestion in hubs like Singapore and Hong Kong occasionally disrupts supply chains.
DocShipper info
From North America to Europe and Asia‑Pacific, trade lanes face different challenges, rate volatility, port congestion, and regulation shifts. DocShipper helps you navigate them all with tailored freight forwarding solutions, multimodal strategies, and up‑to‑date market intelligence.
Whether you’re optimizing intra‑EU deliveries, U.S.–Asia imports, or cross‑regional distribution, our experts ensure cost control, reliability, and end‑to‑end visibility.
🌍 Plan your next shipment with confidence. Talk to one of our logistics specialist.
Future Outlook: Q1 2026 and Beyond
The freight market is being shaped by both immediate post-holiday rate pressures and longer-term structural shifts that will redefine global logistics in the years ahead
Early predictions for post-holiday freight rates
Freight rates are set to face significant downward pressure in early 2026 due to typical post-holiday slowdowns. Container volumes usually fall 15–25% between January and February as retailers cut back imports after the peak season.
Chinese New Year factory closures in late January will deepen this lull. If Red Sea disruptions ease and Suez Canal flows normalize, ocean spot rates could hit new lows, potentially dropping below $1,000/FEU on some Asia–Europe lanes.
The broader structural issue remains ocean overcapacity: supply is expected to grow around 8%, while demand lags at roughly 3%. Once transit times stabilize, this imbalance will continue to pull rates downward.
Air freight should soften as well, though not as sharply. Rates are likely to stay 10–15% above pre-pandemic levels, supported by resilient cross-border e-commerce activity.
In North America, truckload rates may slip 5–8% from Q4 levels as seasonal demand cools. However, ongoing carrier exits and the upcoming produce season should keep the market relatively balanced.
Long-term trends shaping the freight industry
Structural shifts will reshape freight market dynamics beyond 2026, including accelerating decarbonization mandates that raise European shipping costs by 5-15%, driven by IMO Carbon Intensity Indicator rules and the EU Emissions Trading System. Technology adoption (digital platforms, autonomous trucks, AI forecasting) yields 10-20% efficiency gains but remains uneven, with smaller carriers trailing larger players.
Supply chain diversification via the “US Plus One” approach is becoming permanent, increasing complexity but enhancing resilience to geopolitical and policy shocks. Regulatory complexity is escalating across freight modes, ocean decarbonization mandates, stricter trucking emissions and AV rules, and evolving e-commerce air cargo regulations, creating both compliance costs and early-mover opportunities.
Conclusion
Navigating Q4 2025 freight rates means balancing shifting trends across transport modes. Ocean freight keeps sliding under persistent overcapacity despite Red Sea disruptions, while air freight stays firm, driven by e-commerce. In North America, trucking tightens as seasonal demand meets capacity exits.
Success hinges on flexibility, diversifying carriers, using data-driven procurement, and adopting real-time tech tools. Looking to 2026, ocean rates may stay under pressure if routes normalize, air freight should hold strong, and trucking is set for a gradual stabilization. DocShipper helps businesses control freight costs and sustain reliability with multimodal solutions, customs support, and data-backed market insights.
Read More
Looking for more? These articles might interest you:
FAQ | Freight rate forecast Q4 2025: What to expect
Freight rates depend on a base rate adjusted by key variables such as distance, weight, volume, and transport mode.
Typical pricing combines:
Total Cost = Base Rate + Fuel + Congestion + Accessorials − Discounts.
Fuel surcharges often add 20–30%, while congestion fees in busy ports (like Singapore) can add 5–10% or $100–$500 per container.
While freight rate forecasts for late 2025 show downward pressure, 2026 could see modest increases of 2-5% across modes, driven by capacity tightening and recovering demand. Truckload rates may rise due to carrier exits and seasonal produce rebounds, but ocean freight rate forecasts remain low if Red Sea routes normalize, potentially dipping below $1,000/FEU. Air rates could stabilize 10-15% above pre-pandemic levels amid e-commerce growth. However, ongoing tariffs and decarbonization mandates might accelerate hikes in Europe by 5-15%. Shippers can hedge by diversifying routes.
From May 2025, the new Mediterranean ECA sulfur cap (0.10%) will raise fuel costs by 15–20% as ships switch to low‑sulfur fuel or install scrubbers. At the same time, the EU ETS expansion covers 70% of maritime emissions, adding roughly $200–$500 per container. Together, these measures could lift European freight rates by 5–15%, with the strongest impact on Asia–Europe routes. Compliance and fuel strategy will be key cost drivers in 2025.
Spot rates are short-term and volatile, often lower due to overcapacity (e.g., ocean spots down 15-20%), while contract rates provide long-term stability at higher fixed prices for committed volumes. Spot suits flexibility; contracts ensure predictability. Use a 60/40 mix for balance.
Need Help with Logistics or Sourcing ?
First, we secure the right products from the right suppliers at the right price by managing the sourcing process from start to finish. Then, we simplify your shipping experience - from pickup to final delivery - ensuring any product, anywhere, is delivered at highly competitive prices.

Fill the Form
Prefer email? Send us your inquiry, and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Contact us